Midterm 01
Multiple Choices Questions (10 pts)
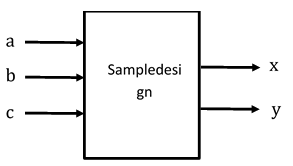
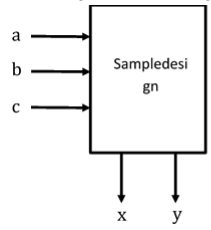
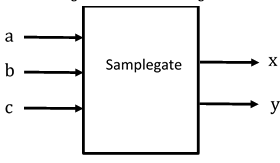
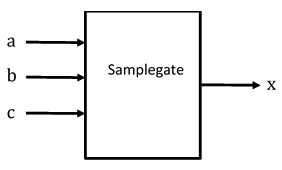
- (2 pts) Which of the following block diagrams represents the given Verilog code?
module Sampledesign (a, b, c, x, y);
input a, b, c;
output reg x, y;
…
endmodule
| a. | b. | c. | d. |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
- (2 pts) For the given Verilog code snippet, identify ZZZ.
module Gate (p, q, r, y);
input p, q, r;
output reg y;
ZZZ
begin
y = p & q & ~r;
end
endmodule
- a.
always @ (p, q, r) - b.
always @ (y) - c.
always (p, q, r) - d.
always (y)
- (2 pts) Identify a true statement about the given Verilog code snippet?
module Example (f, g, h);
input f, g;
output reg h;
always @ (f, g)
begin
f = g & h;
end
endmodule
- a. If g = 1 and h = 0, then f = 0. The change in h’s value to 1 will not execute the procedure; thus, f = 0
- b. When none of the inputs change, the always procedure does not execute
- c. When none of the inputs change, the always procedure still executes
- d. If g = 0 and h = 0, then f = 0. The change in g’s value to 1 causes the procedure to execute f = 1
- (2 pts) Which XXX and YYY complete the structural Verilog description for the given circuit?
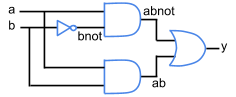
|
|---|
module circuit(a, b, y);
input a, b;
output y;
wire bnot, anotb, abnot;
NOT1 NOT1_2(b, bnot);
AND2 AND2_1 XXX;
AND2 AND2_2 YYY;
OR2 OR2_1(abnot, ab, y);
endmodule
- a. XXX: (abnot, y) and YYY: (ab, y)
- b. XXX: (a, bnot) and YYY: (a, b)
- c. XXX: (a, bnot, abnot) and YYY: (a, b, ab)
- d. XXX: (a, bnot, y) and YYY: (a, b, y)
- (2 pts) Which XXX completes the given structural Verilog code that implements a 4-bit 4x1 mux using 2x1 mux components?
module mux4(d0, d1, d2, d3, s, y);
input [3:0] d0, d1, d2, d3;
input [1:0] s;
output [3:0] y;
XXX
mux2 M1(d0, d1, s[0], low);
mux2 M2(d2, d3, s[0], high);
mux2 M3(low, high, s[1], y);
endmodule
- a. wire [1:0] low, high;
- b. wire [3:0] low, high;
- c. wire [1:0] y;
- d. wire [3:0] y;
Short-Answer Questions (40 pts)
- (5 pts) Perform the following number-system conversions (show your work):
- a. $864_{10} = ()_{2}$
- b. $1011011_{2} = ()_{10}$
- c. $0F100_{16} = ()_{8}$
- d. $1011101111101_{2} = ()_{16}$
- (5 pts) Draw the XOR(x,y) gate CMOS transistor circuit. Show the conduction path and output value when:
- a. x = 1 and y = 0
- b. x = 1 and y = 1
-
(5 pts) Write the 8-bit signed-magnitude, two’s-complement representations for each of these decimal numbers: +19, -47, 0.
-
(5 pts) Expand F(w,y,z) = w’y + yz + w to
- a. sum-of-minterms form
- b. product-of-maxterms form
-
(5 pts) A network router connects multiple computers together and allows them to send messages to each other. If two or more computers send messages simultaneously, the messages “collide” and the messages must be resent. Using the combinational design process, create a collision detection circuit for a router that connects 4 computers. The circuit has 4 inputs labeled M0 through M3 that are 1 when the corresponding computer is sending a message and 0 otherwise. The circuit has one output labeled C that is 1 when a collision is detected and 0 otherwise.
-
(5 pts) Prove or disprove the following proposition: Let X and Y be boolean expressions. Then X · Y = 0 and X + Y = 1 implies that X’ = Y'.
-
(5 pts) Implement a 1-bit 2-to-1 multiplexer using only 2-input NOR gates.
- a. Derive the truth table.
- b. Derive the product-of-sum expression.
- c. Convert the product-of-sum circuit into NOR gate implementation.
- (5 pts) Sketch the circuit that computes $|A - B| × 4$ , where A, B are 4-bit signed (2’s complement) numbers. For example: $𝐴 = 1010, 𝐵 = 0111 \rightarrow |𝐴 − 𝐵| \times 4 = 13 \times 4 = 52$ . You can only use full adders and logic gates. Your circuit must avoid overflow. (hint: In Verilog, $X \times 4$ can be implemented as {X, 2b'00} )