) is the unit of resistance
) is the unit of resistance
 resistor
resistor
 resistor, the current
is 500uA
resistor, the current
is 500uA
 uses 0.25W.
uses 0.25W.
 ) is the unit of resistance
) is the unit of resistance
 resistor
resistor
 resistor, the current
is 500uA
resistor, the current
is 500uA
 uses 0.25W.
uses 0.25W.
 resistor designed to handle up to 1W.
How much voltage can I put across it? What is the current at
that voltage?
resistor designed to handle up to 1W.
How much voltage can I put across it? What is the current at
that voltage?

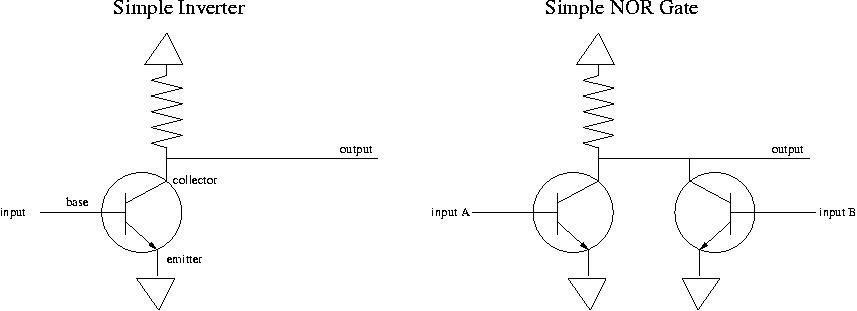
a transistor (in saturation mode) is a switch: